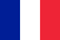
Psoriasis can occur in various forms.Psoriasis options include vulgar (simple, ordinary) or, otherwise, psoriasis plaques (psoriasis vulgaris, plaque psoriasis), psoriasis pustule, surfaces with psoriasis, flexer psoriasis) (flexible psoriasis).This section provides a brief description of any variety of psoriasis along with its code according to the International Disease Classification (ICD-10).

Plush -shaped psoriasis. or Ordinary psoriasis, vulgar psoriasis, simple psoriasis (psoriasis vulgaris) This is the most common form of psoriasis.It is observed in 80% - 90% of all patients with psoriasis.The plush vulgar psoriasis is most often manifested in the form of typical areas raised above the surface of the healthy skin of the areas of inflamed, red, hot skin, covered with gray or silver-white, easily discarded, flaky, dry and thickened skin.The red skin under an easily removed gray or silver layer is easily injured and bleeding as it contains a large number of small vessels.These areas with typical psoriatic damage are called psoriatic plaques.Psoriatic plaques tend to increase in size, merge with adjacent plaques, forming the entire plate of the slab ("paraffin lakes").
Psoriasis on flexion surfaces (flexible psoriasis). or "Back Psoriasis". It usually looks smooth, not peeling or with minimal peeling, red sore spots that are not particularly protruding above the surface of the skin, located exclusively in the folds of the skin, in the absence or minimal lesion of other areas of the skin.Most often, this form of psoriasis affects the folds in the external genital organs, in the groin, on the inner surface of the thighs, axillary depression, folds under obesity of the stomach (psoriatic panus) and on the folds of the skin under the mammary glands in women.This form of psoriasis is particularly susceptible to worsening under the influence of friction, injury to the skin and sweat and is often accompanied or complicated by a secondary fungal infection or streptococcal pyoderma.
Guttat psoriasis (psoriasis) It is characterized by the presence of a large amount of small, raised above the surface of healthy skin, dry, red or purple (to purple), similar in shape of drops, tears or small dots, circles of the elements of the lesion.These psoriatic elements usually strengthen large surfaces of the skin, most often the hips, but can also be observed on the legs, forearms, shoulders, hair of the head, back, neck.Death psoriasis often develops or exacerbates after streptococcal infection, in typical cases - after streptococcal tonsillitis or streptococcal pharyngitis.
Pustular psoriasis or Exudation psoriasis It is the most severe skin skin of psoriasis and looks like bubbles or blisters raised above the surface of healthy skin, filled with unfortunate, transparent inflammatory exudate (pustules).The skin below and above the surface of the pustules and around them is red, hot, edematous, inflamed and thickened, easily exfoliated.The secondary infection of the pustules can be observed, in which case the exudate becomes purulent.Pustus psoriasis can be restricted, localized, while its most frequent localization is the distal ends of the limbs (arms and legs), that is, the lower legs and forearm, this is called palmoplantar pustules (palmoplantar pustulose).In other, more severe cases, pustular psoriasis can be summarized as the widespread spread of pustules over the entire surface of the body and the tendency of fusion into larger pustules.
The causes of psoriasis
Disturbed barrier function of the skin (more special, mechanical trauma or irritation, rubbing and pressure on the skin, abuse of soap and preparation, contact with solvents, household chemicals, solutions containing alcohol, also plays the role of infected foci on the skin or skin allergies, excessive skin) also plays a role in the development of development.
Psoriasis - This is in many ways idiosyncosy skin disease.The experience of most patients suggests that psoriasis may spontaneously improve or, conversely, worsen for no apparent reason.Studies of various factors related to the onset, development or exacerbation of psoriasis tend to be based on the study of small, usually hospitals (not outpatient patients), which is obviously more severe groups of patients with psoriasis.Therefore, these studies often suffer from insufficient sample representation and the inability to identify causal relationships in the presence of a large number of others (including still unknown or unsure) factors that can affect the nature of psoriasis.Often, contradictory finds are found in various studies.Nevertheless, the first signs of psoriasis often occur after stress (physically or mentally), skin damage in places with the first type of psoriatic rashes and/or transmitted streptococcal infection.Conditions, according to a number of sources that can contribute to exacerbation or worsening of psoriasis, include acute and chronic infections, stress, climate change and seasons change.In particular, some drugs, lithium carbonate, beta-blockers, antidepressants, antimalarial drugs, anticonvulsants, according to a number of sources, are associated with psoriasis worsening or can even cause its main occurrence.Excessive consumption of alcohol, smoking, overweight or obesity, malnutrition can weigh the course of psoriasis or complicate its treatment, cause exacerbations.Hair lacquer, some creams and handles, cosmetics and perfumes, household chemicals can also cause psoriasis exacerbation in some patients.

Patients suffering from HIV infection or AIDS often suffer from psoriasis.This seems to be paradoxical for psoriasis researchers, since treatment aimed at reducing the number of T -cells or their activity usually helps to treat psoriasis and HIV infection, or, in addition, AIDS is accompanied by a reduction in the number of T cells.However, over time, with the progression of HIV infection or AIDS, an increase in viral load and a decrease in the number of circulating CD4+ T cells, psoriasis in infected with HIV patients or patients with AIDS worsen.In addition to this mystery, HIV infection is usually accompanied by a severe shift of the cytokine profile to Th2, while vulgar psoriasis in uninfected patients is characterized by severe displacement of the cytokine profile to Th1.According to the current hypothesis, reduced amount and pathologically altered activity of CD4+ T-lymphocytes in patients with HIV infection or AIDS cause hyperactivation of CD8+ T-lymphocytes that are responsible for the development or aggregation of psoriasis in HIV-infected or patients with.However, it is important to know that most patients with psoriasis are healthy in connection with HIV and HIV infection is responsible for less than 1 % of psoriasis cases.On the other hand, psoriasis occurs in HIV-infected people, according to various sources, with a frequency of 1 to 6 %, which is approximately 3 times higher than the frequency of psoriasis in the general population.Psoriasis in patients with HIV infection, and especially AIDS, is often extremely difficult and is poorly occupied or does not succumb to standard methods of therapy at all.
Psoriasis most often develops in patients with initially dry, thin, sensitive skin than in patients with oily or well -enhanced skin and is much more common in women than in men.In the same patient psoriasis, it most often occurs in areas with dry or thinner skin than in oily skin, and especially often occurs in places of damage to the skin, including meetings, teams, scratches, cuts, in places subjected to rubbing, pressure and contact with aggressive supplies, cleaning supplies, cleaning supplies, cleaning supplies, cleaning supplies, cleaning supplies, cleaning supplies and supplies, cleaning supplies, cleaning supplies and supplies.solvents.(This is called a kebner phenomenon).This psoride psoride phenomenon of psoriasis is mainly with dry, thin or injured skin, associated with the infection with the fact that the body infects (probably the most often streptococcus) easily penetrates the skin with minimal skin secretion (which, under other conditions, protects the skin from infections) or in the presence of skin damage.Thus, the most favorable conditions for the development of psoriasis are opposite to the most favorable conditions for the development of fungal infection of the legs (the so -called "leg of the athlete") or armpits, the inguinal region.For the development of fungal infections, the most favorable, wet skin, for psoriasis, on the contrary, dry.Infection,Penetrated into dry skin, causes dry (non -expansion) chronic inflammation, which in turn causes symptoms characteristic of psoriasis, such as itching and increased skin cell proliferation.This, in turn, leads to more increasing dry skin, both due to inflammation and increased proliferation of keratinocytes, and due to the fact that the infected body consumes moisture, which would otherwise serve to moisturize the skin.In order to avoid excessive dry skin and reduce the symptoms of psoriasis, patients with psoriasis are not recommended to use a towel and exfoliants, especially firm as they not only damage the skin, leaving microscopic scratches, but to distort the skin from the skin and the skin from the skin.It is also recommended to use talc or baby swelling after washing or bathing to absorb excess moisture from the skin, which will otherwise "get" an infected agent.It is also recommended to use products that moisturize and nourish the skin, and lotions that improve the function of the sebaceous glands.It is not recommended to abuse soap, detergents.You should try to avoid contact with the skin with solvents, household chemicals.
Diagnosis of psoriasis
The diagnosis of psoriasis is usually simple and is based on a characteristic type of skin.There are no diagnostic procedures or blood tests specific to psoriasis.Nevertheless, with an active, progressive psoriasis or its severe course, blood tests can be found, confirming the presence of an active inflammatory, autoimmune, rheumatic process (increase in rheumatoid factor titles, acute phase proteins, leukocytosis, increased ESR, etc.), as well.Occasionally, skin biopsy is required to exclude other skin diseases and histological confirmation (verification) of the diagnosis of psoriasis.During a Biopsy of the Patient with Psoriasis, Clusters of the So-Called Tears of Retail, Thayer of Keratinocytes, Their Histological Imature, Massive Sun-LordCells, Signs of Increased Proliferation of Keratinocytes and Immunocompetent Cells, Accelerated angiogenesis in a layer of skin under the skin under layer under layer under laying skin under the skin layer under the skin under layer under the skin under the skin.Another characteristic sign of psoriasis is the point bleeding and the ease of bleeding from the skin under the plaque during its sawdust, which is related to both the acceleration of angiogenesis and the pathologically increased permeability and fragile skin vessels in the lesion (symptom of Aushpitz).
Alternative treatment of psoriasis
For the symptomatic treatment of vulgar psoriasis, some of the countries in some countries use ichthiotherapy in some resorts with open thermal springs.The Ruffy Fish, which live there, eat the skin of psoriatic plaques without touching healthy areas.After such treatment, an improvement in the condition of patients with six months or more is observed.The successful location in the subtropics allows you to combine a break in comfortable hotel rooms with fish and sea baths procedures.At your request, the hotel chef will prepare a special diet.The water in the Garra Rufa fish is transmitted to a three -stage cleaning system (mechanical, flowing ultraviolet sterilization and biological purification).The sun, the sea, the clean air, the special diet-all in the complex helps to achieve a positive effect from the bathrooms with miraculous fishing.Daily sprinkling with a mixture of powdered sugar and potato starch will help you remove psoriatic plaques.
Treatment of psoriasis with folk remedies
- To deal with psoriasis, Give up fat, pork, smoking, chocolate, spices, alcohol, coffee and sweets.Enrich the diet with fermented dairy products, fresh herbs, roasted apples, salads for fish and nettle.Eat a lot of vegetable oils rich in essential fatty acids) and products containing lecithin.
- Eat food When boiled, boiled or stewed (off fried and smoked) from the diet.
- Refuse food that increases the acidity in the body- give preference to products that alkalize the body.Some people on the web repeatedly testify that only a change in nutrition in the direction of alkalization contributes to the complete restoration of health not only from the psoriasis itself, but also to old chronic diseases.
- Washing Only children's or tar soap, regular baths with decoction of celandine, hops and three -colorane violets.
- Follow Surgery (hunger 1-2 days).